On your Windows computer, you are linked to your wifi network, but you are unable to access the internet. Your wireless network appears to be secured rather than connected when you check it; there is no Internet secured.
Table of Contents
How to Fix the “No Internet Secured” Error
Encountering the “No Internet Secured” error can be frustrating, especially when you need to be online. This guide provides various methods to resolve this “No Internet Secured” issue, from simple fixes to more advanced troubleshooting steps.
1. Restart your router and computer
Often, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Restarting your router and computer can resolve “No Internet Secured” issues.
- Unplug your router from the power source.
- Wait for about 30 seconds.
- Plug the router back in and wait for it to restart fully.
- Restart your computer and check the connection.
2. Use Network Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in network troubleshooter to help diagnose and fix “No Internet Secured” problems.
- To get started, head to the Start menu search bar, and type in Settings to open Windows Settings.
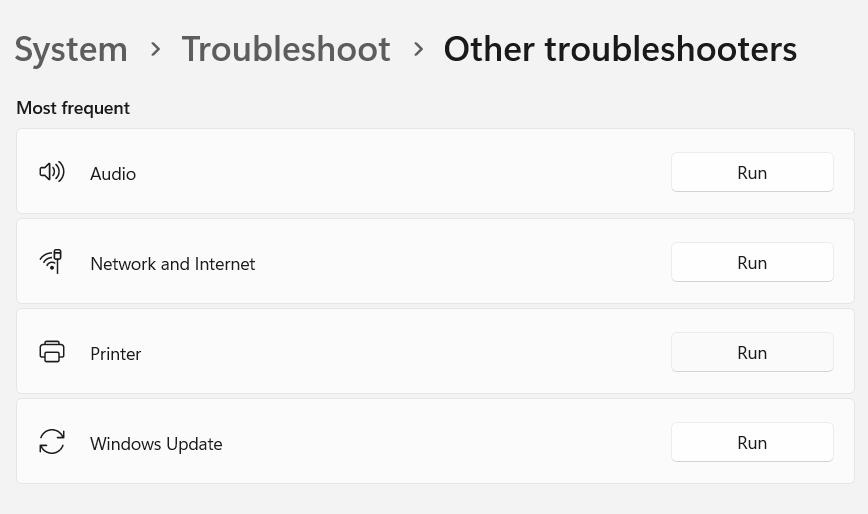
- On the Settings app, click on System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.
- Click the Run button for Internet Connections. Windows will launch the troubleshooter and show the issues for which Windows can troubleshoot.
- Apply the fixes and check for any improvements.
3. ‘Forget’ the internet connection
Forgetting and reconnecting to your Wi-Fi network can sometimes resolve the “No Internet Secured” issue.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi.
- Select the network causing issues and “Manage known networks.“
- click “Forget“.
- Reconnect to the network by entering the password.

4. Fix Connection Properties
Ensure your connection properties are correctly configured.
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to Network & Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter options.
- Right-click your network connection and select “Properties“.
- Check settings under the “Networking” tab.
- Confirm the following are checked:
- Client for Microsoft Networks
- File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks
- Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
- Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)
- Link-layer Topology Discovery Responder

5. Change your Wi-Fi properties
Adjusting your Wi-Fi properties can improve connectivity.
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to Network & Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter options.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi connection and select “Properties“.
- Select “Configure” and navigate to the “Advanced” tab.
- Adjust settings such as “Wireless Mode” and “Roaming Aggressiveness“.

6. Disable and re-enable the network adapter
Disabling and then enabling your network adapter can resolve “No Internet Secured” error.
- Open Device Manager (Right-click Start > Device Manager).
- Expand “Network adapters“.
- Right-click your network adapter and select “Disable“.
- Wait a few seconds, then right-click again and select “Enable“.

7. Refresh Your IP Configuration
Refreshing your IP configuration can resolve “No Internet Secured” issues.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type
ipconfig /releaseand press Enter. - Type
ipconfig /renewand press Enter.
8. Perform a Winsock Reset
A Winsock reset can fix “No Internet Secured” issues related to network sockets.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type
netsh winsock resetand press Enter. - Restart your computer.
9. Restart the Network Setup Service
Restarting this service can resolve network configuration issues.
- Press
Win + R, typeservices.msc, and press Enter. - Find “Network Setup Service“, right-click, and select “Restart“.

10. Reset the Network Settings
Resetting network settings can resolve “No Internet Secured” network-related issues.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Advance Network Settings.
- Click on “Restart Now” under “Network reset” and follow the instructions.

11. Set “Obtain DNS Server Address Automatically”
Ensure your computer is configured to obtain DNS server addresses automatically.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Change adapter options.
- Right-click your network connection and select “Properties“.
- Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click “Properties“.
- Ensure “Obtain DNS server address automatically” is selected.

12. Update Network Adapter Driver
Outdated drivers can cause connectivity issues.
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run box.
- Type devmgmt.msc and click OK to open Device Manager.
- In the Device Manager window, expand the Network adapters section. It will list all the network drivers installed on your computer. Do the following for all of the wireless network drivers.

- Right-click on the wireless network driver and choose Uninstall Driver. Uncheck the “Attempt to remove the driver from this device.” option in the pop-up if it shows up.

- Go to the top menu in Device Manager and under the Action tab, select Scan for hardware changes.
- The driver should appear back in the Display adapters list. If it does not, then restart your PC and it will appear back.
- Right-click on the wireless network driver again and choose Update Driver.
- Select Search automatically for drivers. Windows will scan for available driver updates and download them.
- Restart your PC to apply the changes.

- If it didn’t work, again right-click on the display driver and choose Update Driver but this time select Browse my computer for driver software.
- Then select Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer.
- Select the driver you want to install, generally, it is the pre-selected top option in the list and click Next.
- Restart your PC to apply the changes.

- If even that doesn’t work, you can try going to your laptop or wireless network card manufacturer’s official website and download the latest drivers for your specific model from there and then install the drivers and restart your PC to apply the changes.
13. Reinstall the network drivers
Reinstalling drivers can resolve “No Internet Secured” issues.
- Restart your computer; Windows will reinstall the driver automatically.
- From the list that appears, right-click the Windows icon in your taskbar and choose Device Manager.
- Locate the Wi-Fi driver for your machine by opening the Network adapters option in the Device Manager window. Although the name varies from computer to computer, try searching for terms like Wireless Network Adapter and Wi-Fi 6.
- Select Uninstall device with a right-click on the driver.
- Select the option to “Delete the driver software” (Windows 10) or “Attempt to remove the driver” (Windows 11) in the pop-up window that displays, and then click “Uninstall.“
- Give your computer a restart.

14. Uninstalling the last Windows Update
If you are experiencing issues after installing an update, consider checking for solutions or waiting for Microsoft to release a fix for the “No Internet Secured” problem.
- Go to the Windows Settings.
- Click “Windows Update” from the left-hand side menu.
- Then go to the Update history > Uninstall Updates.

15. Disable your VPN
If simply disconnecting doesn’t work, try disabling the VPN software entirely.
- Open the VPN application.
- Turn it off or exit the application completely.
16. Create a restore point
Creating a restore point before making major changes can help you revert if something goes wrong.
- Press the Windows key + S and type “System Restore” in the search bar.
- Select Create a restore point from the search results.

- Click on System Restore under the “System Protection” tab.

- It will prompt you to select a certain date and open the restoring window.

- If you previously created a restore point, you should utilize it; otherwise, the computer will display a recommended date for restoration. Then click “Finish” to complete the process.
- The finishing time is a few minutes. When finished, your computer will reboot.
17. Fix via registry editor
Be cautious when editing the registry; it can affect system stability.
- Press
Win + R, typeregedit, and press Enter. - Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet. - Make sure the following values exist in the right pane of the Internet:
- “ActiveDnsProbeContent”=”8.8.4.4”
- “ActiveDnsProbeContentV6″=”2001:4860:4860::8844”
- “ActiveDnsProbeHost”=”dns.google”
- “ActiveDnsProbeHostV6″=”dns.google”
- “ActiveWebProbeHostV6″=”www.msftconnecttest.com”
- “EnableActiveProbing”=”1”

18. Disable IPv6 Address
Disabling IPv6 can sometimes resolve “No Internet Secured” issues.
- Select the Start option.
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to Network & Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter options.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi connection and select “Properties“.
- Click OK after unchecking the Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) box.
- When prompted, restart your computer.

19. Set a New DNS Server
Using a public DNS server can improve connectivity.
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to Network & Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter options.
- Right-click your Wi-Fi connection and select “Properties“.
- Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click “Properties“.
- Enter a public DNS server (e.g., Google DNS: 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4).

20. Flush/Clear DNS Cache
Flushing the DNS cache can resolve connectivity issues.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type
ipconfig /flushdnsand press Enter.
21. Check Firewall/Antivirus Settings
Firewalls and antivirus programs can sometimes block internet access.
- Press the Win key to open the Start Menu.
- Type Windows Security and press Enter.
- Choose Firewall & network protection from the left panel.
- Choose the Private network option.
- Disable the toggle under Microsoft Defender Firewall.
- If UAC pops up, click on Yes.
- Check if the problem continues. If yes, just enable the Firewall again.

22. Scan for Malware
Malware and viruses can cause “No Internet Secured” error. To check for issues, conduct a complete computer scan using an authorized antivirus or antimalware tool. Make sure your antivirus software is up to date. You can download a free Malware detector tool.
- Type “Windows Security” in the Windows search bar and select “Windows Security” from the results.
- In the Windows Security window, click on “Virus & Threat Protection.“
- Under “Current threats,” click on “Quick Scan” to perform a basic scan.
- For a more comprehensive scan, you can choose “Full Scan.“
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the scan.
- If any threats are detected, Windows Defender will provide options to remove or quarantine them.

23. Update Windows
Keeping Windows up-to-date can resolve “No Internet Secured” issues.
- Press Win + I to open the Windows Settings.
- Click on Update & Security.
- In the Update & Security window, click on Windows Update in the left-hand menu.
- Click on Check for updates and let Windows search for and install any available updates.
- After the updates are installed, restart your computer and check if the brightness control function keys are functioning correctly.

24. Windows Update troubleshooter
Windows includes built-in troubleshooters to automatically identify and fix “No Internet Secured” problems.
- Open Settings by searching on Windows Search for Settings.
- Choose Troubleshoot under the System tab.
- Click on Other troubleshooters.
- Click on Run next to Windows Update.
- The update troubleshooter will pop up and look for any available issues.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to remove the detected problems from the system.

25. Check for software conflicts
Software conflicts can cause “No Internet Secured” issues.
- Uninstall any recently installed software that might be causing conflicts.
- Restart your computer and check the connection.
26. Proxy server settings
Incorrect proxy settings can affect internet access.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Proxy.
- Ensure “Use a proxy server” is turned off.

27. Disable the Fast Startup option
Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature facilitates a quicker PC restart following a shutdown.
- To launch the Run dialogue box, press the Windows key + R.
- Type “powercfg.cpl” and press Enter.
- In the Power Options window, click on “Choose what the power buttons do” on the left side.
- Click on “Change settings that are currently unavailable“.
- Scroll down and check the box next to “Turn off fast startup“.
- Click on “Save changes“.


28. Change your Power Plan settings
This may result in network connection problems that prevent access to the Internet, such as the “No Internet, Secured” error.
- Open the Control Panel and select Large icons.
- Pick Power Options.
- Click Change plan settings.
- Click on Change Advanced Power Settings.
- Verify that Maximum Performance is selected under Wireless Adapter Settings -> Power Saving Mode.
- Select Apply to shut off the windows.

29. MAC Address filtering
Ensure your router is not blocking your device’s MAC address.
- Log into your router’s admin panel.
- Check the MAC address filtering settings.
- Add your device’s MAC address if necessary.
By following these steps, you should be able to resolve the “No Internet Secured” error and restore your internet connection. If the “No Internet Secured” issue persists, contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for further assistance may be necessary.





